Over time, these groups of migratory humans became isolated from one another, and eventually mutation and other evolutionary pressures produced slight genetic changes, some of which are responsible for the differences in appearance we've commonly used to divide up human beings into racial groups. But periods of isolation were followed, as trade and transportation were developed, by periods of admixture -- the mixing of populations that had previously been separate.

Map of human migratory patterns over the past 100,000 years. A map of the migrations of early humans, as reconstructed via DNA studies. By tracing slight changes in DNA and by combining that data with a calculation of the rate at which genetic material changes over time, researchers have been able to reconstruct the general pattern of the historical migrations of peoples across the globe, starting in East or South Africa and extending north into Europe and Asia and eastward to the Pacific Islands and through the Americas, to the tip of South America. The research indicates that all humans alive today share a couple of common ancestors, a woman who lived in Africa around 150,000 years ago, and a man who lived in Africa around 60,000 years ago, at around the time human beings began to leave Africa to explore the rest of the world.
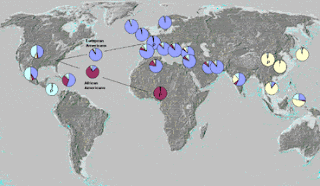
Considering that commonality, it's no surprise the amount of variation between even the most disparate groups of human beings is very small. It's estimated that people share some 99.9% of their DNA. Even looking at that .1% that does vary, 85% of the variation that has been observed is unconnected to membership in any particular group of people; only 15% of the variation is between defined groups. In fact, because as a species we spent the most time in Africa, the greatest amount of genetic variations are currently found among people living on the African continent -- on a genetic level, an individual of East African ancestry may have more in common with a European than with a West African.
© 2006 Educational Broadcasting Corporation. All Rights Reserved.


No comments:
Post a Comment